
What Is Spatial Analysis in GIS? A Practical Guide for Land Development
In land development and urban planning, understanding spatial relationships is essential.
Spatial analysis, powered by Geographic Information Systems (GIS), transforms raw geographic data into insights that support better decisions.
This guide explains what spatial analysis in GIS is, why it matters in land development, and how Eliot Sinclair applies it to deliver accurate, data-driven outcomes across New Zealand.
20 Nov 2025 | 4 min read
Understanding Spatial Analysis
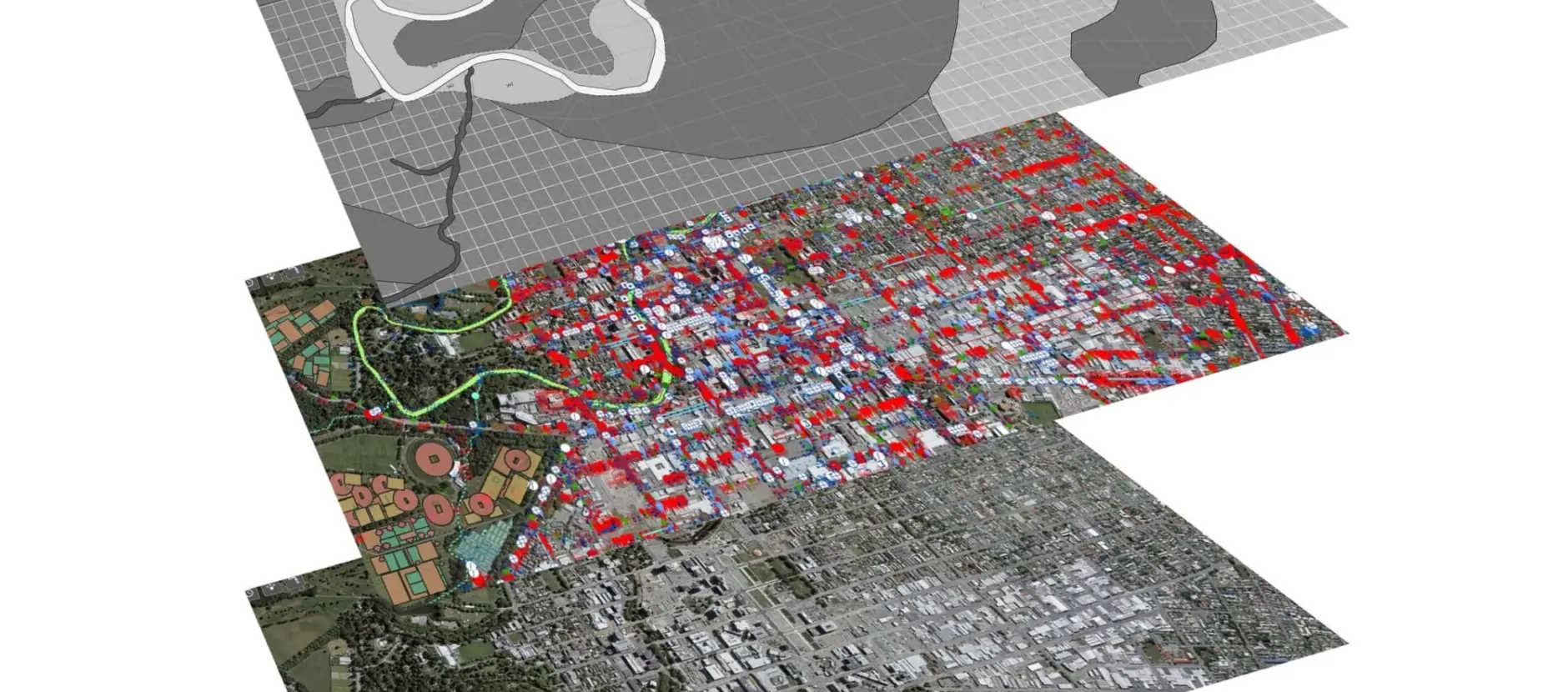
What Is Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis is the process of examining the locations, attributes, and relationships of features in geographic data to uncover patterns and insights.
It goes beyond mapping. Spatial analysis uses statistical and modelling techniques to identify clusters, predict trends, and test different scenarios. This helps planners and engineers make informed, evidence-based decisions.
Why Spatial Data Matters
Spatial data is the foundation of every GIS project. It represents real-world features through coordinates, allowing us to model the earth’s surface and understand how different elements relate to one another.
Whether it is vector data showing property boundaries or raster data representing elevation, spatial data enables precise and reliable analysis.
At Eliot Sinclair, our GIS specialists ensure that every dataset is accurate and up to date, because sound data underpins sound decisions.
Applications in GIS
GIS platforms such as ArcGIS combine data, analysis, and visualisation tools into one system. They enable professionals to:
- Assess site suitability
- Model environmental constraints
- Plan transport corridors
- Map and manage infrastructure assets
As GIS technology evolves, spatial analysis continues to advance. Today, it incorporates sophisticated modelling, interpolation, and even machine learning to deliver deeper insights and more predictive capabilities.
The Role of GIS in Spatial Analysis
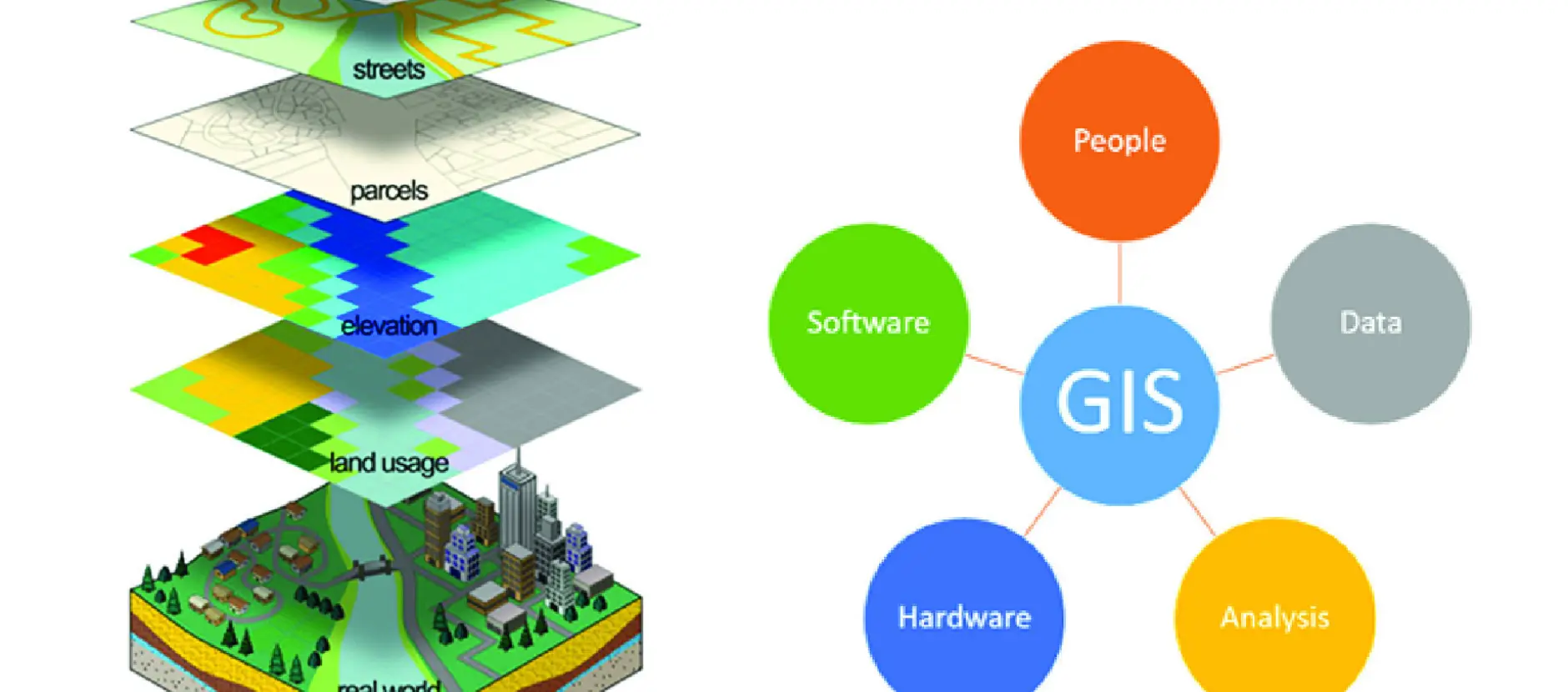
Overview of Geographic Information Systems
GIS is the backbone of modern spatial analysis. It combines software, hardware, and geographic data to map and analyse relationships that would otherwise be difficult to see.
From vector layers (points, lines, and polygons) to raster imagery (satellite or aerial data), GIS allows professionals to visualise how terrain, land use, and infrastructure interact. This understanding supports more effective and sustainable design.
Core Spatial Analysis Techniques
Common spatial analysis methods include:
- Buffering: defining impact zones around key features
- Overlay analysis: combining datasets to assess constraints or opportunities
- Network analysis: modelling routes and connectivity for roads or utilities
- Spatial statistics: identifying clusters, outliers, and spatial correlations
These tools reveal how one decision affects another across a landscape. Eliot Sinclair applies these techniques to provide tailored insights for developers, councils, and infrastructure clients across New Zealand.
Using ArcGIS for Spatial Analysis
ArcGIS is one of the most widely used platforms for geospatial analysis. Its processing and visualisation tools enable everything from basic spatial queries to advanced 3D modelling and scenario testing.
The strength of ArcGIS lies in its ability to handle both vector and raster datasets, enabling users to layer different information types and uncover relationships that might otherwise go unnoticed. Planners, engineers, and analysts can use ArcGIS to:
- Run spatial queries to locate specific features or measure distances between them
- Overlay datasets to identify environmental constraints or development opportunities
- Perform terrain analysis using elevation data to understand slope, aspect, and drainage
- Model spatial scenarios that predict how land use, population growth, or infrastructure changes will affect an area over time
- Visualise results in maps, 3D environments, or dashboards that make complex data easy to interpret
ArcGIS Pro, the desktop version of the software, includes powerful geoprocessing tools that support statistical analysis, network modelling, and predictive mapping. Users can automate workflows, test multiple design scenarios, and integrate data from external sources such as LiDAR surveys or satellite imagery.
With the rise of cloud-based GIS, ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise now allow teams to collaborate in real time, publish interactive web maps, and share insights across organisations. This makes it easier for planners, surveyors, and decision-makers to work from the same reliable data source and maintain version control.
By combining these analytical and visualisation tools, ArcGIS helps transform raw geographic data into information that supports better decisions. Whether that’s selecting a site for development, assessing environmental risks, or managing existing assets.
Spatial Analysis Work in Land Development
Benefits of Spatial Analysis in Planning
Spatial analysis is a powerful tool for land development planning. It allows professionals to:
- Visualise the potential impact of a project, such as how a new subdivision interfaces with existing infrastructure or natural features.
- Identify risk areas early, such as zones susceptible to flooding, steep slopes, or unstable ground and adapt the design accordingly.
- Model different development scenarios and compare options around transport, utilities, zoning or environmental overlays—to find the most efficient, compliant solution.
- Align projects with regulatory, environmental and community objectives by using spatial data to support sustainable, resilient outcomes.
By embedding spatial analysis in the planning phase, development teams are better positioned to minimise costs, manage uncertainty and streamline approvals.
Case Studies in New Zealand Land Development

Case Study: Christchurch Infill Subdivision
Eliot Sinclair supported KVF Goulds Ltd with a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary approach to developing a small residential subdivision on a site with uneven terrain.
- Spatial data and GIS played a pivotal role in:
- Enabling efficient planning, design, and delivery.
- Integrating detailed topographical survey data within a GIS framework to accurately model existing ground conditions and assess re-levelling requirements and optimise lot layouts to minimise earthworks.
- Visualising multiple design scenarios, ensuring the most cost-effective and buildable layout was achieved while maintaining high-quality section outcomes for buyers.
The result: GIS integration improved collaboration between planning, engineering, and surveying disciplines, providing a single, data-driven source of truth throughout the project. This allowed for rapid adjustments and informed decision-making within tight timeframes. The precision of GIS-enabled cut and fill calculations reduced the need for imported or exported material, saving both time and cost.
Read the full case study: Efficient Design and Collaboration for Residential Site Development
Conclusion
Spatial analysis sits at the heart of modern land development. By connecting geographic data with on-the-ground design decisions, it allows planners, surveyors and engineers to see the full picture and understand how each element of a project interacts with its surroundings.
From identifying risks and constraints to modelling design outcomes, GIS and spatial analysis provide the clarity needed to make confident, data-driven decisions. As projects grow in complexity, the ability to translate spatial data into practical solutions becomes increasingly valuable.
At Eliot Sinclair, our team combines technical expertise with a deep understanding of New Zealand’s planning environment to help clients make the most of their spatial information.
If you’re planning a development or need guidance on how spatial analysis could support your project, get in touch with our team. We’ll help you turn data into insight, and insight into confident action.
More Insights

International Women’s Day 2026 | Christchurch
24 Feb 2026
Eliot Sinclair is proud to host our third annual…
The Four Main Systems of GIS
02 Feb 2026
The Short Answer: Hardware, Software, Data and…

Warren Haynes on 40 Years at Eliot Sinclair
15 Dec 2025
Warren Haynes has been part of Eliot Sinclair for…